Table of Contents
List of Figures
List of Tables
- 1.1. Revision History
Table of Contents
This document assumes that the reader understands PHP and has a basic understanding of what Amazon's S3 service is.
Table of Contents
fs3 is an Amazon S3 compatible client and server implementation enabling central ized file storage web services ideal for multi-server applications. Users can de velop potential S3-based applications using only a typical Apache-PHP environmen t.
fs3 is not a replacement for Amazon's S3 service. fs3 runs on a user-controlled server and the API is a subset of Amazon's offering focusing on file management with real files, not databases. The objective is to provide the minimal key services, fast and reliably, usinga typical Apache web server installation. Amazon offers a very robust service with customer support and more features.
Web sites that have the space and bandwidth can use fs3 for file management scalability with multiple servers and have the ability to move to Amazon's solution when demand requires it.
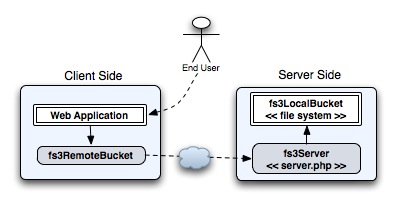
The fs3 remote client fs3RemoteBucket is
compaible with Amazon's S3 service, so switching between the fs3 server
and Amazon's system will be easier. Amazon S3 clients may be compaitble
with fs3 out of the box.
fs3 is not a replacement for Amazon's S3 service! It is intended to allow developers and engineers build robust systems for use on service clusters without the expense of using the clusters until it is actually needed. It is because of Amazon's robust design that it was chosen as a model platform.
These operations are all that most applications require.
Object GET requests using REST API.
Object PUT requests using REST API.
Object DELETE requests using REST API.
Bucket GET requests using REST API with prefix option.
Bucket PUT requests using REST API.
Bucket DELETE requests using REST API.
Authentication is a direct model of Amazon's.
Error reporting.
fs3 Home Page: http://fs3.sourceforge.net/
Source Forge Project: https://sourceforge.net/projects/fs3/
User Guide: http://fs3.sourceforge.net/userGuide.html
Developer Guide :http://fs3.sourceforge.net/devGuide.html
API Documentation: http://fs3.sourceforge.net/fs3Api/
Source Repository: http://fs3.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/fs3/
Downloads: https://sourceforge.net/project/showfiles.php?group_id=300336
The MIT License
Copyright (c) 2010 Thomas Davis
(sunsetbrew)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
"Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit
persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the
following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall
be included in all copies or substantial portions of the
Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY
KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN
NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM,
DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR
OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE
USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Please report bugs, request features or support using the tracker at http://sourceforge.net/tracker/?group_id=300336. Using this interface will help others who may see the issue and help the project team prioritize and remember it.
As it says in the license, this software is "AS IS". While the project team wants to provide the best software, it does not constitute a waver in the license.
Table of Contents
Extract the fs3 archive somewhere on the target system.
From within the existing web application use the
fs3RemoteBucketfor connecting to a remotely hosted web service. Refer toexamples/client.phpfor reference.Alternatively
fs3LocalBucketcan be used for connecting to a local repository. Moreover, afs3RemoteBucketcan be added as a read-only master to enable a very nice development connection which grabs the data remotely while only adding files to local repository.
Extract the fs3 archive somewhere on the target system.
Copy the
examples/server.phpinto the Apache web server docroot.Copy the
examples/htaccess.cfginto the Apache web server docroot as.htaccess. This will redirect all requests to theserver.phpscript.Create a repository directory to store the objects in. It must be writable by the web server, but does not need to be in the docroot.
Update the configuration of
server.php.For production use, the
fs3MockKeyManagerin server.php must be configured to contain the usable keys.
Table of Contents
This project is based on the Amazon Simple Storage Service. Please refer to the See the Amazon Simple Storage Service Developer Guide [AMAZON-S3] for more details on how the client/server communications works.
Provide a fast and simple file storage service for use with any number of clients.
Provide support for developing against large production repositories without the need for copying the respository. This method must protect and forbid modication the production data.
Maintain web service compatibility with Amazon's S3 service such that using fs3 can be a migration path to use S3.
Easy to deploy and use.
Do not require a database.
Backwards compatibility must be supported in future versions.
Use Amazon's authentication framework.
The API must be stateless. It must not prevent the use of distributed solutions.
The API must minimize use of system resources.
Local transactions take place through immediate function calls just like any software library.
User calls a method on
fs3LocalBucketwhich performs actions against a local directory and returns the result synchronously to the user.
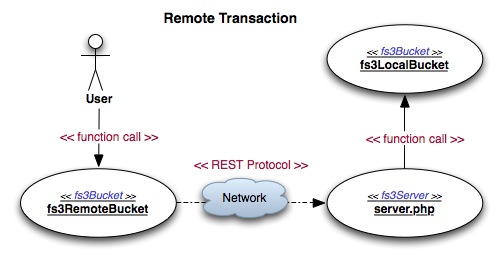
Remote transactions take place over a network connection. The flow
includes two different fs3Bucket
implementations and one service.
User calls a method on
fs3RemoteBucketwhich uses a network based protocol (REST) to communicate the request to a remote service.The remote service then makes the appropriate method call on
fs3LocalBucketwhich performs actions against a local directory.The remote service takes the result and returns the result synchronously to the user.
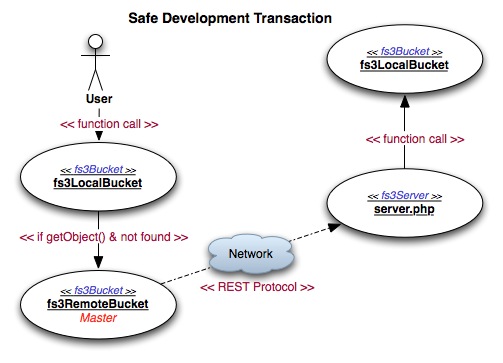
A development is a mix of Local and Remote transactions so that all writing is limited to local but reading is done remotely if not found locally first. This is near perfect arrangment for projects with huge file stores and a nead to ensure development instances do not write to the production file stores.
User calls a method on
fs3LocalBucketwhich performs actions against a local directory and returns the result synchronously to the user.If the call is to
getObject()and the Object cannot be found locally, thefs3LocalBucketwill call its read-only master assignedfs3RemoteBucketto get the object remotely. This uses a network based protocol (REST) to communicate the request to a remote service.The remote service then makes the appropriate method call on its own
fs3LocalBucketwhich performs actions against its local directory.The remote service takes the result and returns the result synchronously to the user.
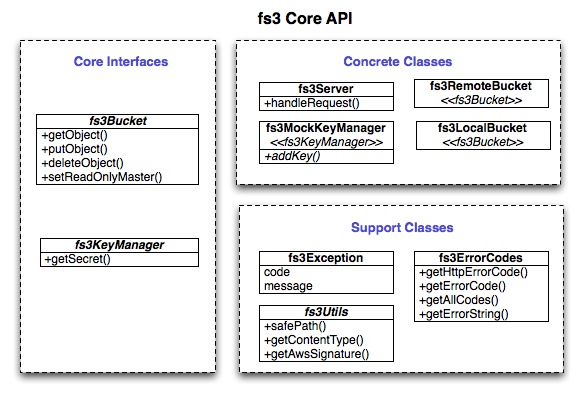
fs3Bucket- This interface defines all the methods needed to support object storage and retrieval.fs3KeyManager- This interface defines all the methods needed to cross reference between keys and secrets for request authentication.fs3Server- This class encapsulates server-side request handling.fs3MockKeyManager- This class is a simple array based implementation of key manager for use with fs3Server.fs3RemoteBucket- This class implements client-side interface of the API to a remote fs3 or Amazon S3 service.fs3ObjectInfo- This class implements a plain object containing general object information.fs3LocalBucket- This class implments the S3 repository using the local file system. In this context, a bucket is simply a directory and the objects are files in that directory tree.fs3Exception- This class encapsulates the all fs3 exceptions. As of this writing, it is the same as the default Exception with a different name.fs3ErrorCodes- This class encapsulates all of Amazon's S3 error codes. The class has contants for all known errors and methods for coverting from error name, error codes and HTTP response codes.fs3Utils- This class ecapulates code that is common to both the client and server implmentations. There is no real boundary for this class.
Table of Contents
The user authentication state machine.
This section covers the configuration of authentication keys on the server.
This API replicated Amazon's S3 method for authenication. Please refer to the Amazon Simple Storage Service Developer Guide [AMAZON-S3] for more details on how the authentication works.
Authentication is composed of 4 basic portions.
Key: string used to identify the user. Very much like a name only it will look more like a junk string. This key is known by the client and sent ot the server as part of the message. The server then uses this key to lookup the secret.
Secret: 40 character string used to create a "signature". There is one secret per key. It is known by the client and never sent in the message. The server can find it using the key.
Signature: a string alorithmically gernerated from the message contents and the secret. It is sent along with the message to the server. The server then creates its own signature from the secret it looks up and compares them to ensure there is an exact match.
Message Contents: Information from the message used when creating a signature. This includes the date, resource name, checksum, amazon headers, content type and HTTP method.
Server-side only
The fs3KeyManager interface defines the
methods the fs3Server will use to cross reference
between keys and secrets.
The class fs3MockKeyManager provides the most
trival of implmentation using only an array for cross referencing.
However, the data still must be populated from somewhere. It is up to the
user to do this.
It would be nice to have a database to store keys in or at least a data file; however, the goal of this project is to keep it simple. It is easy enough to implement the one method interface.
Table of Contents
This section for the developers working in the fs3 project.
The source code is stored in the Subversion resposity hosted by Source Forge. There are a wide variety of tools available for managing code in Subversion.
The active respository is located at https://fs3.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/fs3/trunk/ and is free for any person or company to check out. Like any software project, authorization is required to check in changes. Changes are encouraged and completely welcome. Just contact the project owner to get the needed authorization.
Coding and style conventions can leads to a reduction in creativity and fun. Developers learn what other people have done and make their own informed choices. Thus far, the majority of conventions used on this project are described in article PHP Application Development Part One [FELLS-PHP]. It is only there to help the developer understand why some things were done a certain way.
Table of Contents
This section describes the documentation strategy.
phpDocumentor is used to process the API documentation directly from the PHP source code.
phpDocumentor behaves much like JavaDoc and Doc++. It looks for comment blocks starting with /** and uses them for documentation. It also has the smarts to pick apart the source code itself even without comment blocks. Finally it searches comment blocks for tags that start with the @ symbol. The tags can tell it what to do or provide special information like what an argument type and meaning is. See the phpDocumentor web site [PHPDOC-ORG] for more information.
pear install XML_Parser
pear install XML_Util
pear install XML_Beautifier
pear install PhpDocumentor
DocBook version 5.0 is the file format for the User and Developer guides. It is an XML format that is easy to maintain and convert to many other formats. There are a lot of editors for DocBook documents. One such editor is the XMLmind XML Editor which was used to create this document. See DocBook.org [DOCBOOK-ORG] from more information.
There are so many of these tools out there and attempts to choose just one, especially one that runs on all platforms to make design diagrams easier failed. It was hard to find a good free one. Since the original developer already owned a license to OmniGraffle, that is in use for now.
Table of Contents
The How To Test Guide.
This project uses pear package PHPUnit to run the unit tests. See the PHPUnit web site [PHPUNIT-DE] for more details on how to use it.
By all tests we mean, all tests that don't need require connection.
cd tests phpunit --verbose AllTests
The test suites are in the tests directory and have names ending
with Test.php by convention.
cd tests phpunit FileIWantToTest.php
Table of Contents
This section contains a list of references used in this document.
Online Resources
[AMAZON-S3] Amazon Web Services LLC. Amazon Simple Storage Service Developer Guide.
[PHPDOC-ORG] phpDocumentor.
[PHPUNIT-DE] PHPUnit.
[DOCBOOK-ORG] DocBook.org. OASIS DocBook Technical Committee.
[FELLS-PHP] PHP Application Development Part One. Developer Shed. 03 March 2005.